This cheat sheet provides a guide to using a tape measure, including its parts, measurement markings, and reading methods. Whether you're working on construction, DIY projects, or tailoring, this will help you understand how to read a tape measure correctly. The included image makes interpreting fractional inches easier.
Parts of a Tape Measure
Blade
The long, flexible metal or fabric strip with measurement markings.
Hook (Tang)
The metal end that moves slightly to ensure accurate internal and external measurements.
Lock Mechanism
A button or slider that holds the tape in place after extending.
Belt Clip
A metal clip attached to the casing for easy carrying.
Housing (Case)
The outer shell that protects the tape, often made of plastic or metal.
Measurement Markings
Imperial System (Inches and Feet)
- Inches: Marked with whole numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Half-Inches (½"): The second-longest lines between whole inches.
- Quarter-Inches (¼", ¾"): Slightly shorter lines between half-inch marks.
- Eighth-Inches (⅛", ⅜", etc.): Smaller lines dividing quarters.
- Sixteenth-Inches (1/16", 3/16", etc.): The smallest lines on most tapes.
- Foot Marks (' or ft): Typically in bold or red, every 12 inches.
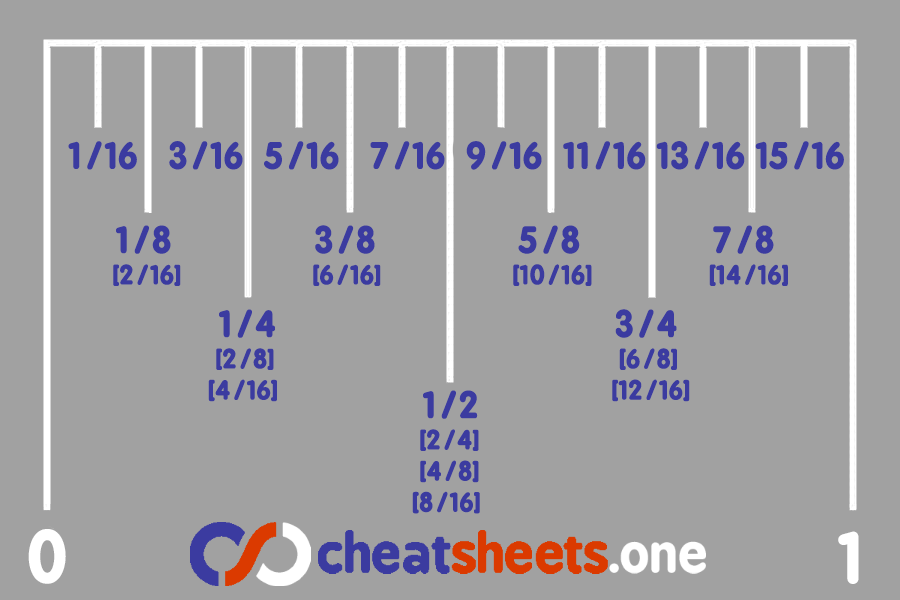
How to Read an Inch-Based Tape Measure
The image below illustrates fractional inch markings, showing how each segment represents a fraction of an inch:
Metric System (Centimeters and Millimeters)
- Centimeters (cm): Marked with whole numbers.
- Millimeters (mm): Smallest divisions (10 mm per cm).
Stud and Rafter Marks
- 16-inch spacing: Red markings often indicate standard stud spacing.
- 19.2-inch spacing: Common for rafter layouts.
How to Read a Tape Measure
Reading in Inches
- Identify the whole-inch mark.
- Count the smaller increments for fractions of an inch.
- If needed, convert fractions to decimals (e.g., ½" = 0.5").
Reading in Centimeters and Millimeters
- Identify the whole centimeter.
- Count millimeters beyond the cm mark.
- If necessary, convert mm to cm (10 mm = 1 cm).
Special Features on Tape Measures
Self-Retracting
The tape automatically coils back into the housing when released.
Magnetic Hook
Helps secure the tape to metal surfaces for one-person use.
Dual Measurement
Displays both metric and imperial units.
Fractional Readout
Some tapes show fractions (⅛, ¼, etc.) for easy reading.
Measuring Techniques
Inside Measurement
Use the hook against an interior surface and push the tape measure to the opposite side.
Outside Measurement
Hook the tape onto an object’s edge and pull outward.
Measuring Circles and Curves
Use the flexible tape to wrap around curved surfaces and read where the tape meets itself.
Measuring Heights
Extend the tape vertically and lock it in place to measure heights accurately.
Tips and Sources
Useful Tips
- Always keep the tape straight to avoid inaccurate measurements.
- Use the hook’s movement to get precise internal and external dimensions.
- Measure twice, cut once—double-check your measurements.
- If using a retractable tape, control its return to avoid damage.
- For long measurements, use a helper or secure the tape’s hook.
